Database Analysis and Design
Before we start the database design for contacts, lets have a look at Google Contacts, which is our original inspiration to start this project. We have added a new contact with randomly generated name, address and phone number.
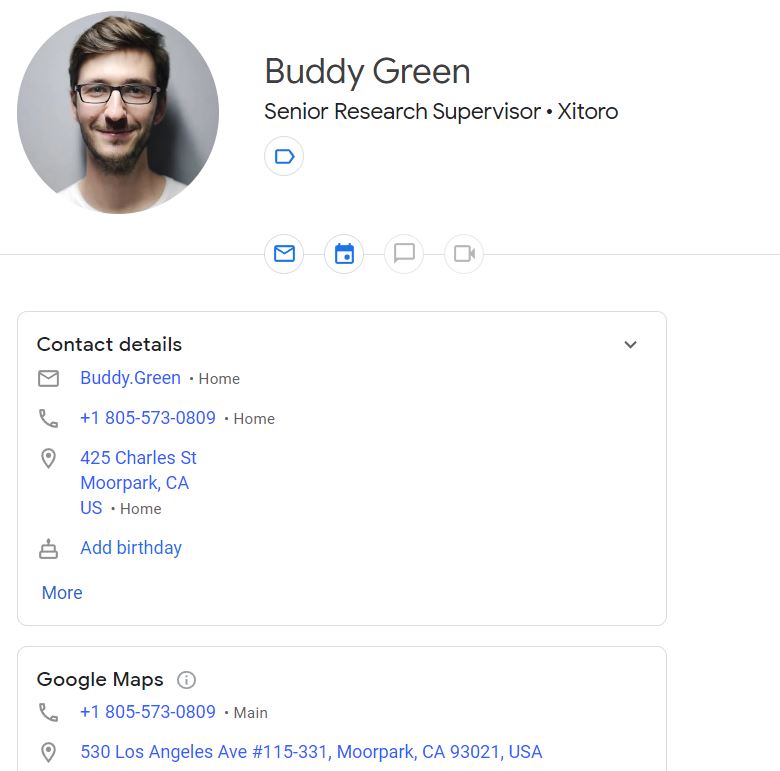
A contact will obviously have First Name, Middle and Last Name. In Google contacts, we can also save his company name, job title and department. We cannot save job history, there are not multiple company information for a contact, we can save only one company, job title and department.
We can save multiple email addresses for a single contact. Each email address can optionally have a label. You can click on + button and keep adding multiple email addresses. So there is one to many relationship between Contact and Emails. We also have email labels, which need to be defined in a separate table like EmailLabel.
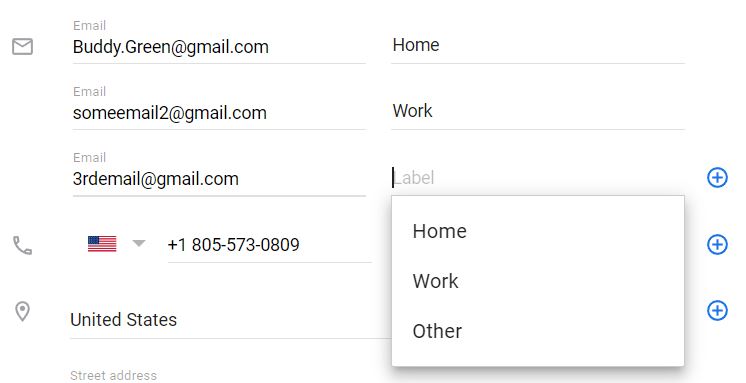
Similarly we can also save multiple phone numbers for a contact. Each phone number may have optional phone label. Click on + button to keep adding multiple phone numbers. So there will also be one to many relationship between Contact and Phone. And for labels, we will create a separate table PhoneLabel.
We can also add multiple addresses for a contact, which means there is one to many relationship between Contact and Address. Each address has a label, so we need to define the address labels in a separate table. In Google contacts, we can enter free text in city name. For country, there is a dropdown. There is another dropdown for state. When you select country, its relevant states are loaded in state dropdown.
Each contact may also have multiple labels. There will be one to many relationship between Contact and Label. The labels will also need to be defined in separate table.
So based on above analysis, we have come up with the following database design.
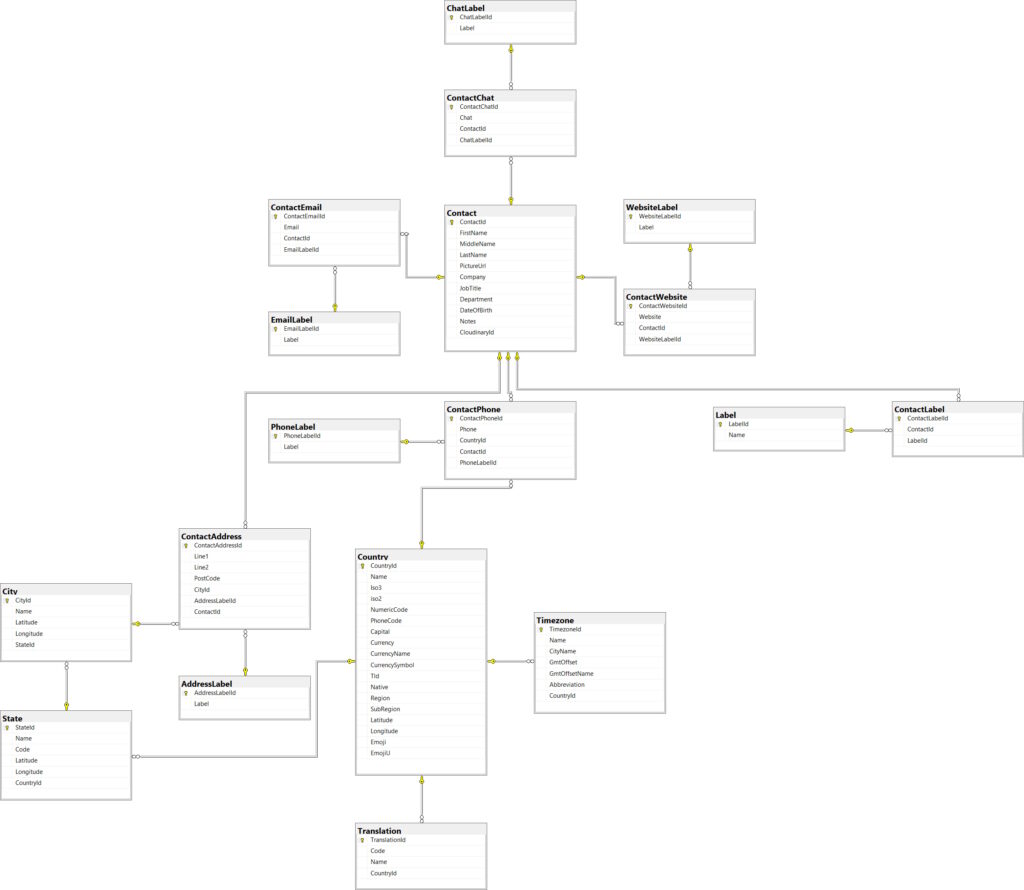
As per above database design, we have total 18 tables to manage the contacts in address book app, having some of the basic features of Google Contacts.
Create Entity Classes
Lets start by creating entity classes for defining labels. First we will add the Label class, which just consists of id and name. Open ASP.NET web API project in Visual Studio, in Entities folder create a new class Label. LabelId is the primary key. Name is required field of type string.
[Table("Label")]
public class Label
{
[Key]
public int LabelId { get; set; }
[Required, MaxLength(20)]
public string? Name { get; set; }
}
In Entities folder add another class EmailLabel. It is also a simple table with EmailLabelId as primary key and Label as required string field.
[Table("EmailLabel")]
public class EmailLabel
{
[Key]
public int EmailLabelId { get; set; }
[Required, MaxLength(20)]
public string? Label { get; set; }
}
In the same pattern add the other labels. Below is the list of all label entities with their GitHub links.
Lets create the Contact entity now. ContactId is the primary key. FirstName is the required field of type string. Only one field is required. All the other fields are optional, means you can just enter first name in the app and save the contact. MiddleName, LastName, PictureUrl etc are of type nullable string.
The contact also has 6 child tables for label, email, phone, address, chat and websites. If a contact has only one phone, we can just add single field in the Contact table. But a contact may have 0 or more phones, so we have to create a separate table for it. And we will create 6 child tables as follows. In Entities folder, create a new class Contact and add the following code.
[Table("Contact")]
public class Contact
{
[Key]
public int ContactId { get; set; }
[Required]
public string? FirstName { get; set; }
public string? MiddleName { get; set; }
public string? LastName { get; set; }
public string? PictureUrl { get; set; }
public string? CloudinaryId { get; set; }
public string? Company { get; set; }
public string? JobTitle { get; set; }
public string? Department { get; set; }
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
public string? Notes { get; set; }
// Child tables
public IEnumerable<ContactLabel>? ContactLabels { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<ContactEmail>? ContactEmails { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<ContactPhone>? ContactPhones { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<ContactAddress>? ContactAddresses { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<ContactWebsite>? ContactWebsites { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<ContactChat>? ContactChats { get; set; }
}
You will get error for the child tables, because they are not created yet. Lets create them now.
We will start with ContactLabel. Create a new class ContactLabel in Entities folder and add the code below. The primary key is ContactLabelId, which is auto generated. It has two fields.
- ContactId – It is mandatory, it is not nullable.
- LabelId – It is also mandatory, it is not nullable.
[Table("ContactLabel")]
public class ContactLabel
{
[Key]
public int ContactLabelId { get; set; }
// Foreign keys
public int ContactId { get; set; }
[ForeignKey(nameof(ContactId))]
public Contact? Contact { get; set; }
public int LabelId { get; set; }
[ForeignKey(nameof(LabelId))]
public Label? Label { get; set; }
}
To understand the relationship between Contact, ContactLabel and Label, have a look at the database design diagram below. Labels are defined in separate table. Contacts exist in its own table. One contact may have 0 or more labels, so we have created a linked table ContactLabel.
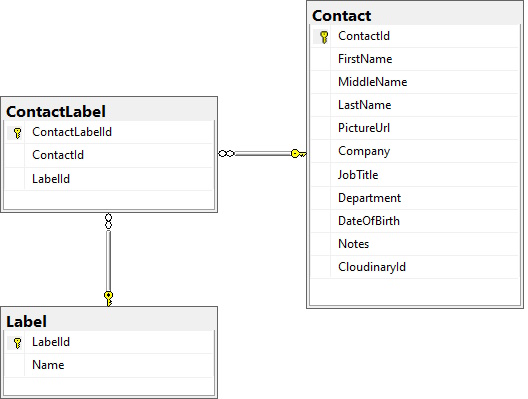
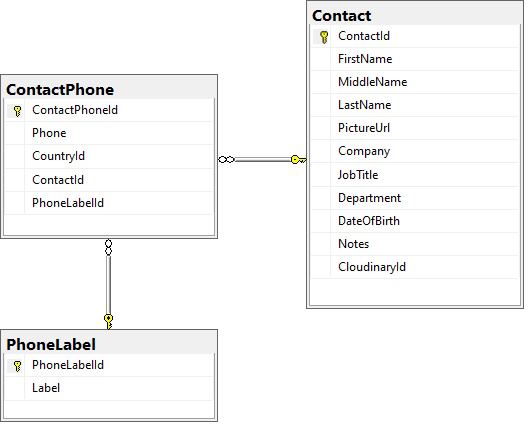
Lets create the ContactPhone entity now. Create a new class ContactPhone in Entities folder and add the code below. ContactPhone has the following fields.
- ContactPhoneId is the primary key, which is auto generated by the database
- Phone – contains the phone number, it is required field, cannot be null. We define such fields with [Required] annotation and string? nullable string type. Default value of string? is null, which will not be valid due to [Required]. If we just use string, default value will be empty string, which will not throw validation error. So for required string we use string? with [Required].
- CountryId – It is optional. It can be null. If it has a value, it must exist in a valid record in the Country table.
- ContactId – It is non-null. Its value must be an existing ContactId from the Contact table.
- PhoneLabelId – It is optional. It can be null. If it has a value, it must be a valid record in the PhoneLabel table.
So with this design, we can just add a phone number like below, just like Google Contacts.
- Add only phone number without country and label
- Add a phone number with a CountryId
- Add a phone number with a PhoneLabelId
[Table("ContactPhone")]
public class ContactPhone
{
[Key]
public int ContactPhoneId { get; set; }
[Required]
public string? Phone { get; set; }
// Foreign keys
public int? CountryId { get; set; }
[ForeignKey(nameof(CountryId))]
public Country? Country { get; set; }
public int ContactId { get; set; }
[ForeignKey(nameof(ContactId))]
public Contact? Contact { get; set; }
public int? PhoneLabelId { get; set; }
[ForeignKey(nameof(PhoneLabelId))]
public PhoneLabel? PhoneLabel { get; set; }
}
To have a better understanding, view the database diagram below.
Similarly create the entity classes for other tables. You can get the code for all entities from GitHub.
Update Database Context
After you have created all the 18 entity classes, add the remaining entities in AppDbContext. Open Data\AppDbContext.cs and update the code as follows.
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public AppDbContext(DbContextOptions<AppDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
// Tables
public DbSet<Country>? Countries { get; set; }
public DbSet<State>? States { get; set; }
public DbSet<Translation>? Translations { get; set; }
public DbSet<Timezone>? Timezones { get; set; }
public DbSet<City>? Cities { get; set; }
public DbSet<Contact>? Contacts { get; set; }
public DbSet<Label>? Labels { get; set; }
public DbSet<ContactLabel>? ContactLabels { get; set; }
public DbSet<ContactEmail>? ContactEmails { get; set; }
public DbSet<EmailLabel>? EmailLabels { get; set; }
public DbSet<ContactPhone>? ContactPhones { get; set; }
public DbSet<PhoneLabel>? PhoneLabels { get; set; }
public DbSet<ContactAddress>? ContactAddresses { get; set; }
public DbSet<AddressLabel>? AddressLabels { get; set; }
public DbSet<ContactWebsite>? ContactWebsites { get; set; }
public DbSet<WebsiteLabel>? WebsiteLabels { get; set; }
public DbSet<ContactChat>? ContactChats { get; set; }
public DbSet<ChatLabel>? ChatLabels { get; set; }
}
Update Database from EF Core Entity Classes
After updating the AppDbContext, open the Package Manager Console in Visual Studio and run the following commands.
add-migration contact-entities
update-database
The project should build successfully and update the SQL Server database.