Our server side is complete, we have created the API in ASP.NET Core. Now we will work on the React app.
Create the Dtos
Open the React app in Visual Studio Code. So far we have created the Dtos for City, State and Country in part one. Now we will create the remaining Contact related Dtos. As usual we have three Dtos for each entity, Response, Edit and Search. In this article we will provide the code snippet of Dtos of three entities. For the remaining you may refer to the GitHub repository.
Dtos for Label Definitions
We have 6 entities for Label definitions. And we will create 6 x 3 = 18 Dtos for the label definitions.
- AddressLabel
- ChatLabel
- EmailLabel
- Label
- PhoneLabel
- WebsiteLabel
Lets take PhoneLabel as an example. Create a new file PhoneLabel.ts in src\Dtos folder and add the following code.
The Dtos we create in React matches the Dtos we created previously in ASP.NET Core web API project.
PhoneLabelRes dto has two members, one for Id and other for the phone label.
PhoneLabelReqEdit has just one member, for phone label. This dto is used for both creating new phone label and editing existing one.
The PhoneLabelReqSearch dto extends the PagedReq class. It does not have its own field. The searchText is member of the parent class PagedReq, which is used to search in label field.
export interface PhoneLabelRes {
phoneLabelId?: string;
label?: string;
}
export class PhoneLabelReqEdit {
label?: string = "";
}
export class PhoneLabelReqSearch extends PagedReq {
constructor(
{
pageNumber = 1,
pageSize = Common.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE,
orderBy = "",
searchText = "",
}: PagedReq,
{}
) {
super({
pageNumber: pageNumber,
pageSize: pageSize,
orderBy: orderBy,
searchText: searchText,
});
}
}
You can create the Dtos for other label definitions on the same pattern. Complete code is available on GitHub.
Dtos for Contact Phone, Label, Address etc.
Contact entity has zero to many relationship with the labels, so we had created linked 6 entities for each label definition e.g. ContactPhone, ContactLabel, ContactAddress etc. We have 6 linked entities and will have 6 x 3 = 18 Dtos for these linked entities.
- ContactPhone
- ContactEmail
- ContactAddress
- ContactLabel
- ContactChat
- ContactWebsite
We will not cover Dtos for all the above entities, we will only share example for ContactPhone dtos.
Lets have a look at the database diagram for ContactPhone again. A Contact may have 0 or more phone numbers, this we have ContactPhone entity.
ContactPhone has its own Id as primary key, Phone for storing the actual phone number. The phone number must belong to a Contact, so it has Contact Id field. A phone number may have an optional label, so it has PhoneLabelId field. A phone number may also have an optional Country Code, so it has CountryId field.
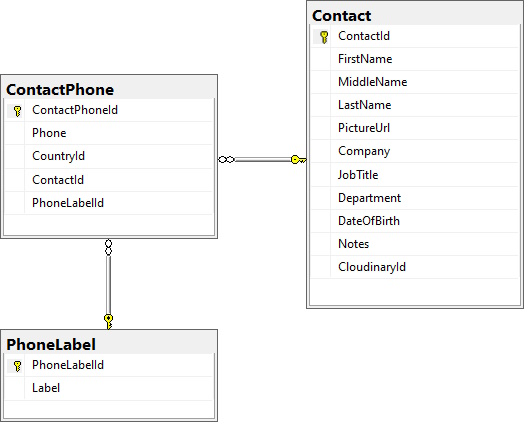
As we created the Dtos for ContactPhone in ASP.NET Core, we will the same in the React app. Below is the code for the 3 Dtos of ContactPhone.
In the Response Dto we have the following
- contactPhoneId – it is the primary key
- phone – contains the actual phone number
- countryId – optional country Id, to lookup for country code
- country – object of type CountryRes, to lookup for country code
- contactId – contains the contact id
- contact – object of type ContactRes – optional
- phoneLabelId – phone label id to lookup the phone label name
- phoneLabel – object of type PhoneLabelRes
In Edit dto, we don’t include the primary key. We only have the phone and foreign keys.
In the search dto, we extend the dto from PagedReq. SearchText and paging related fields are inherited from PagedReq. The response Dto also has contactId field, so that we may search all phone numbers of a specific contact.
export interface ContactPhoneRes {
contactPhoneId?: string;
phone?: string;
countryId?: string;
country?: CountryRes;
contactId?: string;
contact?: ContactRes;
phoneLabelId?: string;
phoneLabel?: PhoneLabelRes;
}
export class ContactPhoneReqEdit {
phone?: string = "";
countryId?: string = "";
contactId?: string = "";
phoneLabelId?: string = "";
constructor(contactId?: string) {
this.contactId = contactId;
}
}
export class ContactPhoneReqSearch extends PagedReq {
contactId?: string;
constructor(
{
pageNumber = 1,
pageSize = Common.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE,
orderBy = "",
searchText = "",
}: PagedReq,
{contactId = ""}
) {
super({
pageNumber: pageNumber,
pageSize: pageSize,
orderBy: orderBy,
searchText: searchText,
});
this.contactId = contactId;
}
}
Dtos for Contact
Lets create the 3 dtos for the main Contact entity. Create a new file Contact.ts in src\dtos folder and add the following code.
All the dtos in React client app must match with the dtos in the ASP.NET Core web API. The response dto has all the fields like firstName, lastName, pictureUrl etc. It also has the arrays for phone number, email, addresses etc.
The edit dto only edits the fields like firstName, lastName, pictureUrl. It does not edit phone number, emails etc.
The search dto extends from PagedReq, as we did in all dtos previously. It also has its own field labelId, so that we can also search all contacts with specific label e.g. search all contacts with label Home, Work etc.
export interface ContactRes {
contactId?: number;
firstName?: string;
middleName?: string;
lastName?: string;
pictureUrl?: string;
company?: string;
jobTitle?: string;
department?: string;
dateOfBirth?: Date;
notes?: string;
contactLabels?: ContactLabelRes[];
contactEmails?: ContactEmailRes[];
contactPhones?: ContactPhoneRes[];
contactAddresses?: ContactAddressRes[];
contactWebsites?: ContactWebsiteRes[];
contactChats?: ContactChatRes[];
}
export class ContactReqEdit {
firstName?: string = "";
middleName?: string = "";
lastName?: string = "";
pictureUrl?: string = "";
company?: string = "";
jobTitle?: string = "";
department?: string = "";
dateOfBirth?: string = Common.formatDate(new Date());
notes?: string = "";
}
export class ContactReqSearch extends PagedReq {
labelId?: string;
constructor(
{
pageNumber = 1,
pageSize = Common.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE,
orderBy,
searchText = "",
}: PagedReq,
{labelId = ""}
) {
super({
pageNumber: pageNumber,
pageSize: pageSize,
orderBy: orderBy,
searchText: searchText,
});
this.labelId = labelId;
}
}
API Helper Methods for Contact and Related Entities
In React, we call the ASP.NET web APIs using helper methods, defined in separate TypeScript ts files. The helper methods uses Axios to call the web APIs. We have encapsulated the calls to Axios and web API Urls in these helper methods. This way our React pages become much simpler, the API calls in React pages look like normal method calls, it simplifies our code greatly.
Lets get started on writing the API helper methods.
API Helper Methods for Label Definition Entities
There are 6 label definition entities, so we will create 6 files for writing API helper methods. In this article, we will only share code of one file, the rest can be viewed on GitHub. Create a new file phoneLabelApi.ts in src\api folder and add the following code.
We have 5 methods in this file, get, update, create, delete and search. All other label definition files will have the same 5 methods.
export const PhoneLabelApi = {
search: async function (searchParams: PhoneLabelReqSearch) {
const response = await api.request({
url: "/phoneLabels/search",
method: "GET",
params: searchParams,
})
return response.data
},
get: async function (phoneLabelId?: string) {
if (!phoneLabelId) return {};
const response = await api.request({
url: `/phoneLabels/` + phoneLabelId,
method: "GET",
})
return response.data
},
create: async function (phoneLabel: PhoneLabelReqEdit) {
const response = await api.request({
url: `/phoneLabels`,
method: "POST",
data: phoneLabel,
})
return response.data
},
update: async function (phoneLabelId?: string, phoneLabel?: PhoneLabelReqEdit) {
await api.request({
url: `/phoneLabels/` + phoneLabelId,
method: "PUT",
data: phoneLabel,
})
},
delete: async function (phoneLabelId?: string) {
const response = await api.request({
url: `/phoneLabels/` + phoneLabelId,
method: "DELETE",
})
return response.data
},
}
API Helper Methods for Contact Phone, Address, Chat etc.
Since we have different entities for ContactPhone, ContactAddress, ContactChat, ContactWebsite, ContactLabel and ContactEmail, we created separate APIs for these in ASP.NET, we will also create separate files for these in React as well.
We will share the code of ContactPhone api, the rest can be accessed from GitHub. In src\api folder, create a new file contactPhoneApi.ts and add the code below. The 5 methods are same as before, which are get, update, create, search and delete. But ContactPhoneApi has anyPhone method. The purpose of anyPhone method is to check whether a phone label is being used in a phone number or not. It will be more clear when we will create the UI.
export const ContactPhoneApi = {
search: async function (searchParams: ContactPhoneReqSearch) {
if (!searchParams.contactId || searchParams.contactId == "") return {};
const response = await api.request({
url: "/contactPhones/search",
method: "GET",
params: searchParams,
})
return response.data
},
get: async function (contactPhoneId?: string) {
if (!contactPhoneId) return {};
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contactPhones/` + contactPhoneId,
method: "GET",
})
return response.data
},
anyPhone: async function (phoneLabelId?: string) {
if (!phoneLabelId) return {};
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contactPhones/anyPhone/` + phoneLabelId,
method: "GET",
})
return response.data
},
create: async function (contactPhone: ContactPhoneReqEdit) {
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contactPhones`,
method: "POST",
data: contactPhone,
})
return response.data
},
update: async function (contactPhoneId?: string, contactPhone?: ContactPhoneReqEdit) {
await api.request({
url: `/contactPhones/` + contactPhoneId,
method: "PUT",
data: contactPhone,
})
},
delete: async function (contactPhoneId?: string) {
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contactPhones/` + contactPhoneId,
method: "DELETE",
})
return response.data
},
}
You can go ahead and create API helper methods for other linked entities as well, in the same pattern.
API Helper Methods for Contact
Now we will create the API helper methods for the Contact, which is our main entity. Create a new file contactApi.ts in src\api folder and add the code below.
As we did in other APIs, we will have get, search, create, update and delete methods for Contact. It has two new methods
- countAddressesByCityId – It returns the number of addresses which have the specified city
- updateImage – It updates the profile picture of a contact. It sends form POST request with uploaded image file data
export const ContactApi = {
search: async function (searchParams: ContactReqSearch) {
const response = await api.request({
url: "/contacts/search",
method: "GET",
params: searchParams,
})
return response.data
},
get: async function (contactId?: string) {
if (!contactId || contactId == "") return {};
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contacts/` + contactId,
method: "GET",
})
return response.data
},
count: async function () {
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contacts/count`,
method: "GET",
})
return response.data
},
countAddressesByCityId: async function (cityId?: string) {
if (!cityId) return {};
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contacts/addressCount/` + cityId,
method: "GET",
})
return response.data
},
create: async function (contact: ContactReqEdit) {
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contacts`,
method: "POST",
data: contact,
})
return response.data
},
update: async function (contactId?: string, contact?: ContactReqEdit) {
await api.request({
url: `/contacts/` + contactId,
method: "PUT",
data: contact,
})
},
delete: async function (contactId?: string) {
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contacts/` + contactId,
method: "DELETE",
})
return response.data
},
updateImage: async function (contactId?: string, fd?: FormData) {
const response = await api.request({
url: `/contacts/` + contactId,
method: "POST",
data: fd,
})
return response.data
},
}