In the second part we added 13 new entities, their related Dtos, then we added 13 new repositories for each entity. We will continue with adding service layer for each repository now.
Interface for PhoneLabel
We have 6 entities/tables for label definitions like phone label, email label etc. We will create service classes for each label. Repository classes only do database and Entity Framework related work. Any operation that is specific to domain or business, must be done in Services.
For creating service, we first define an interface of the service, and then implement the interface in a Service class. Lets take phone label as an example.
In the ASP.NET web API project, create a new interface IPhoneLabelService in the Services folder. Add the following methods definitions in it.
public interface IPhoneLabelService
{
PhoneLabelRes Create(PhoneLabelReqEdit dto);
PhoneLabelRes Update(int phoneLabelId, PhoneLabelReqEdit dto);
void Delete(int phoneLabelId);
PhoneLabelRes Get(int phoneLabelId);
ApiOkPagedResponse<IEnumerable<PhoneLabelRes>, MetaData>
Search(PhoneLabelReqSearch dto);
}
Now these methods look very familiar to the ones we created in the first part, for country, state and city. Every service has methods like Create, Update, Delete, Get and Search.
Service Class for PhoneLabel
Create a class PhoneLabelService in the Services folder. It will inherit from IPhoneLabelService interface. Add the following code in this class. The service class just calls the repository classes for CRUD. We have omitted the code for all methods except the Delete method.
Here we are doing something new. We call a validation method before doing the delete operation. See the screenshots below to first understand the requirements of this validation.
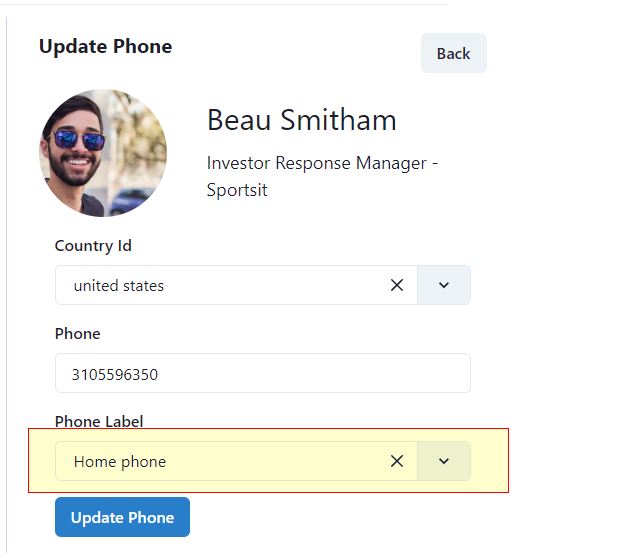
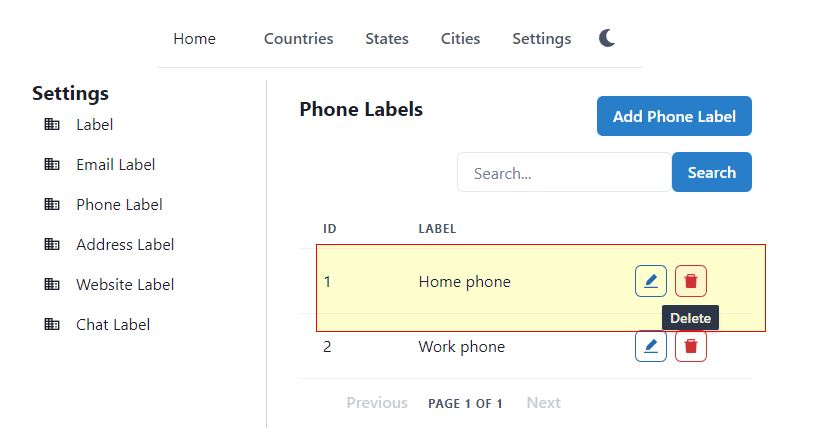
There are two labels shown in the above screenshot, Home phone and Work phone. We have a contact, who has a phone number with “Home phone” label. Should we allow to delete the Home phone label? No. We must first check from the database if that label is being used in some contact or not. If that label is used somewhere, it should not be deleted. With cascade delete, it will also delete the child record. If not cascade delete, then the child record will become orphan, without ID of the parent.
So in the code below, we check whether this labelId is used anywhere in ContactPhone repository. If found, we throw an exception. If you copy the code, you will get error for IContactPhoneService, lets write that next.
public class PhoneLabelService : IPhoneLabelService
{
private readonly IRepositoryManager _repositoryManager;
private readonly IMapper _mapper;
private readonly IContactPhoneService _contactPhoneService;
public PhoneLabelService(IRepositoryManager repositoryManager,
IMapper mapper,
IContactPhoneService contactPhoneService) {}
public PhoneLabelRes Create(PhoneLabelReqEdit dto) {}
public void Delete(int phoneLabelId)
{
ValidateForDelete(phoneLabelId);
var entity = FindPhoneLabelIfExists(phoneLabelId, true);
_repositoryManager.PhoneLabelRepository.Delete(entity);
_repositoryManager.Save();
}
private void ValidateForDelete(int phoneLabelId)
{
if (_contactPhoneService.AnyPhone(phoneLabelId))
{
throw new Exception("Cannot delete phone label. It is being used in some phones.");
}
}
private PhoneLabel FindPhoneLabelIfExists(int phoneLabelId, bool trackChanges) {}
public PhoneLabelRes Get(int phoneLabelId) {}
public ApiOkPagedResponse<IEnumerable<PhoneLabelRes>, MetaData> Search(PhoneLabelReqSearch dto) {}
public PhoneLabelRes Update(int phoneLabelId, PhoneLabelReqEdit dto) {}
}
Controller for PhoneLabel
The API Controller acts as an end point for the web API. As usual our controllers will be dumb and minimal, they will just call the service classes and return the response to the React client.
Note that we did the validation on Delete phone label operation in the Service class. We have Delete methods in 3 places.
- Delete method in controller
- Delete method in service
- Delete in repository
The controller should be dumb, it should only act as a layer between external world (React) and the internal app. Controllers should only do common and built in validations like Required, MaxLength etc. We are already using such validators in Dtos by adding [Requiired] and [MaxLength(20)] annotations on Dto and Entity fields.
The Delete method in the repository PhoneLabelRepository should only deal the database stuff. It should know how to delete data from the SQL Server. It inherits from RepositoryBase, so our base class implements the Delete from database method. Only the Search queries are implemented in individual repository class.
The Delete method in the Service class must make business decisions. For example if a PhoneLabel is being used somewhere, it should throw exception, which must be implemented in the Service. Checking for duplicate must also be implemented in Service. Anything which is not related to database or API endpoint, should be in the Service class. In short, all business and domain related operations must be implemented in the Service classes.
This way, our Repository classes become independent of Service class, we can change the database repository from SQL Server to some other database, by just replacing the repository.
Note that in Service class, we create instance of interface e.g. private readonly IRepositoryManager _repositoryManager. And in program.cs service extension method, we register RepositoryManager class with IRepositoryManager interface. In future if we want to change the database from SQL Server to another, we could create another RepositoryManager e.g. MySqlRepositoryManager, which will implement the same IRepositoryManager interface, and have different methods of creating MySql repositories.
So this way, we don’t have to update the code in 18 service classes and 18 controllers. If we mix database operations with the service, then our business methods will become dependent on the database. By separating the repository, we make the domain (Service) classes independent.
Imaging if we have 180 classes instead of 18. Imaging if we have 1800 classes instead of 18. What if we have 100 entities. When the code grows, we must divide the code in different layers, and try to make each layer independent of each other.
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class PhoneLabelsController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IPhoneLabelService _phoneLabelService;
public PhoneLabelsController(IPhoneLabelService phoneLabelService)
{
_phoneLabelService = phoneLabelService;
}
[HttpGet("search")]
public IActionResult Search([FromQuery] PhoneLabelReqSearch dto)
{
var res = _phoneLabelService.Search(dto);
return Ok(res);
}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Default()
{
return Search(new PhoneLabelReqSearch());
}
[HttpGet("{phoneLabelId}")]
public IActionResult Get(int phoneLabelId)
{
var res = _phoneLabelService.Get(phoneLabelId);
return Ok(res);
}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Create(PhoneLabelReqEdit dto)
{
var res = _phoneLabelService.Create(dto);
return Ok(res);
}
[HttpPut("{phoneLabelId}")]
public IActionResult Update(int phoneLabelId, PhoneLabelReqEdit dto)
{
var res = _phoneLabelService.Update(phoneLabelId, dto);
return Ok(res);
}
[HttpDelete("{phoneLabelId}")]
public IActionResult Delete(int phoneLabelId)
{
_phoneLabelService.Delete(phoneLabelId);
return NoContent();
}
}
Interface for ContactPhone
In Services folder, add a new interface IPhoneLabelService and add the method definitions below. As before, we have CRUD methods, but one new method is there, which is AnyPhone(int phoneLabelId). This method will return true or false based
public interface IContactPhoneService
{
ContactPhoneRes Create(ContactPhoneReqEdit dto);
ContactPhoneRes Update(int contactPhoneId, ContactPhoneReqEdit dto);
void Delete(int contactPhoneId);
ContactPhoneRes Get(int contactPhoneId);
bool AnyPhone(int phoneLabelId);
ApiOkPagedResponse<IEnumerable<ContactPhoneRes>, MetaData>
Search(ContactPhoneReqSearch dto);
}
Service Class for ContactPhone
Create a new class ContactPhoneService in the Services folder and implement the interface as below. We have omitted all the code for CRUD methods, they just call the related repository, you may complete on your own or get the code from GitHub.
The new method here is AnyPhone(). It searches whether there is any record exists with the phoneLabelId or not. If a phone exists with that label, it returns true. This method will be used in two places.
- PhoneLabelService.Delete() method – if label is used in a phone number, don’t delete the label
- ContactPhoneController – we will also expose this method in the web API, so that React app could also check the status when a user wants to delete a label
public class ContactPhoneService : IContactPhoneService
{
private readonly IRepositoryManager _repositoryManager;
private readonly IMapper _mapper;
public ContactPhoneService(IRepositoryManager repositoryManager,
IMapper mapper)
{
_repositoryManager = repositoryManager;
_mapper = mapper;
}
public ContactPhoneRes Create(ContactPhoneReqEdit dto) {}
public void Delete(int contactPhoneId) {}
private ContactPhone FindContactPhoneIfExists(int contactPhoneId, bool trackChanges) {}
public ContactPhoneRes Get(int contactPhoneId) {}
public ApiOkPagedResponse<IEnumerable<ContactPhoneRes>, MetaData> Search(ContactPhoneReqSearch dto) {}
public ContactPhoneRes Update(int contactPhoneId, ContactPhoneReqEdit dto) {}
public bool AnyPhone(int phoneLabelId)
{
return _repositoryManager.ContactPhoneRepository.FindByCondition(
x => x.PhoneLabelId == phoneLabelId,
false)
.Any();
}
}
Controller for ContactPhone
Now lets write the controller for the ContactPhone. Add a new web API controller in the Controllers folder and add the following methods in it. All CRUD related code is same, they just call service classes and return the response to the React client, so we have omitted the code for CRUD methods.
Just the code for AnyPhone method is there, as it is new for us. With this API, the client can check whether a phone label is being used in any phone number of not, it returns true/false value.
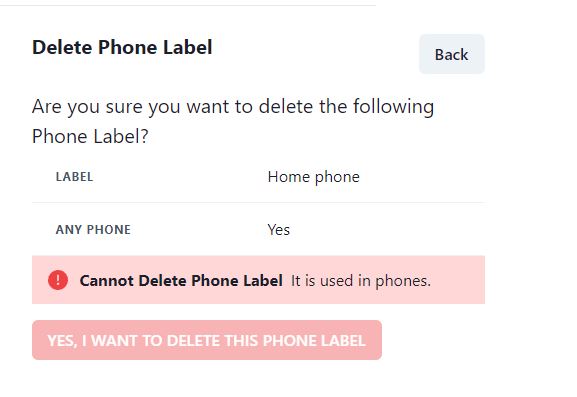
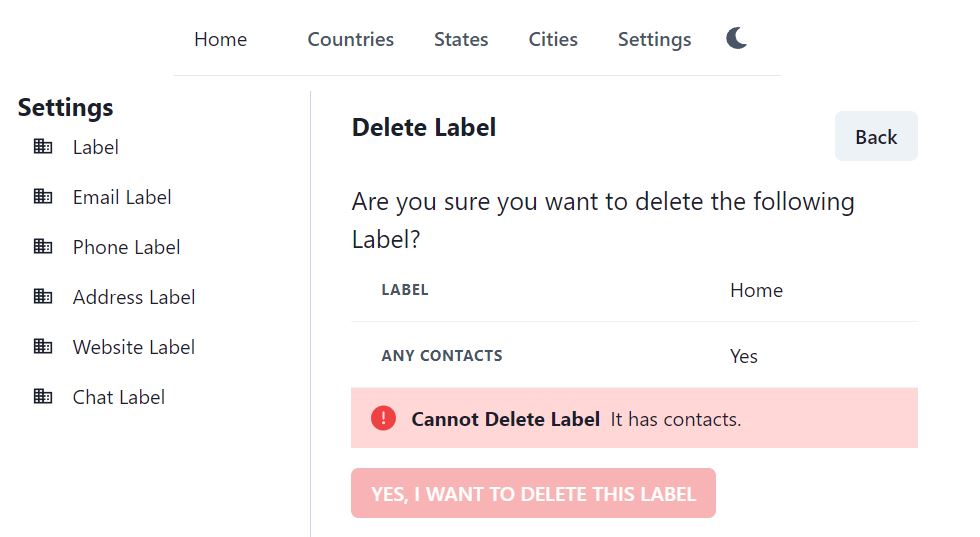
See the screenshot below for the React app, delete phone label screen. The Delete phone label page has Any Phone field, it is “Yes” in the screenshot. An error message is also shown, that you cannot delete this phone label, as it is used in phone numbers.
We could also use Count() method to show the exact count, but Any() method just returns true if even one record is found. It is much more faster than the Count() method. For such delete operation, we don’t even need the Count method, as we are not interested in finding how many phone numbers have this Home Phone label. We just need a Yes//No whether it is safe to delete or not.
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ContactPhonesController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IContactPhoneService _contactPhoneService;
public ContactPhonesController(IContactPhoneService contactPhoneService) {}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Default() {}
[HttpGet("search")]
public IActionResult Search([FromQuery] ContactPhoneReqSearch dto) {}
[HttpGet("anyPhone/{phoneLabelId}")]
public IActionResult AnyPhone(int phoneLabelId)
{
var res = _contactPhoneService.AnyPhone(phoneLabelId);
return Ok(res);
}
[HttpGet("{contactPhoneId}")]
public IActionResult Get(int contactPhoneId) {}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Create([FromBody] ContactPhoneReqEdit dto) {}
[HttpPut("{contactPhoneId}")]
public IActionResult Update(int contactPhoneId, [FromBody] ContactPhoneReqEdit dto) {}
[HttpDelete("{contactPhoneId}")]
public IActionResult Delete(int contactPhoneId) {}
}
To get the complete code of the project, you may download from GitHub.
Service and Controller for Email, Website, Address, Chat and Label
We covered the service and controller for PhoneLabel. There was one thing new, we cannot delete phone label, if it is being used in phone numbers.
The service and controllers for Email, website, address, chat and label will also be implemented in the similar way. The Delete method should have similar validation. An Email label cannot be deleted, if it is being used in an email address. A contact label cannot be deleted, if it is linked with any contact. Similarly addresses also have labels, we cannot delete an address label, if it is being assigned to an address.
Take an example of contact label. A contact Buddy Green has label Home.
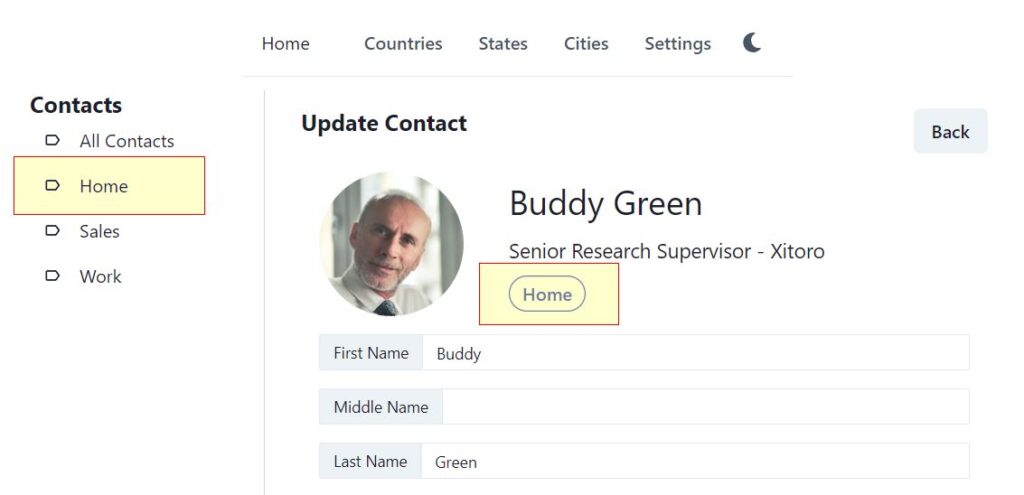
Now click on Settings – Labels – Home – Delete icon. There are few contacts, which are labelled Home. Can we just delete this label?
![]()
The React page calls AnyConact api to find whether this label is used anywhere or not. It gives error message because the contact Buddy Green is labelled Home.
Contact Service
Lets work on the Contact Service now. Contact is our main entity, which has related tables of Phone, Email, Address etc. Lets start by creating the interface for the service. Create a new interface IContactService in Services folder.
public interface IContactService
{
ContactRes Create(ContactReqEdit dto);
ContactRes Update(int contactId, ContactReqEdit dto);
ContactRes UpdateImage(int contactId, IFormFile file, string tempFolderPath);
void Delete(int contactId);
ContactRes Get(int contactId);
int Count();
int Count(int cityId);
ApiOkPagedResponse<IEnumerable<ContactRes>, MetaData>
Search(ContactReqSearch dto);
}
As usual, it has 4 CRUD methods. There are 2 methods for Count. One gets the total number of contacts, other gets the total contacts in a given city. There is a new method UpdateImage, which uploads profile picture of contact. We will write a separate article on uploading the profile picture of the contact.
Now Create a new class ContactService in the same Services folder. It will implement the IContactService interface. Write the code below in the ContactService class.
public class ContactService : IContactService
{
private readonly IRepositoryManager _repositoryManager;
private readonly IMapper _mapper;
private readonly ICloudinaryService _cloudinaryService;
public ContactService(IRepositoryManager repositoryManager,
IMapper mapper,
ICloudinaryService cloudinaryService) {}
{
_repositoryManager = repositoryManager;
_mapper = mapper;
_cloudinaryService = cloudinaryService;
}
// implement methods
}
Since the Contact entity has 6 related tables, it does CRUD on contact and its related entities. We will discuss all the implemented methods one by one. Start with the Create method.
Create and Update Contact
It is similar to the Create methods which were created for all other entities. It receives a Dto ContactReqEdit and creates a new contact. Lets check the ContactReqEdit dto again. The dto for create/edit just has the fields of Contact table. There is no data of related 6 tables!! Create a new contact on Google Contacts, you will note that you can just enter First Name and save, it will create a new contact, with just first name. We implemented the same. All related data like phone, address, email etc. are optional.
public class ContactReqEdit
{
[Required]
public string? FirstName { get; set; }
public string? MiddleName { get; set; }
public string? LastName { get; set; }
public string? PictureUrl { get; set; }
public string? Company { get; set; }
public string? JobTitle { get; set; }
public string? Department { get; set; }
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
public string? Notes { get; set; }
}
We have ContactEmail, ContactPhone and other entities, which are managed by ContactEmailService, ContactPhoneService etc. So ContactService just has to deal with the Contact entity only, at least for the Create and update methods.
public ContactRes Create(ContactReqEdit dto)
{
var entity = _mapper.Map<Contact>(dto);
_repositoryManager.ContactRepository.Create(entity);
_repositoryManager.Save();
return _mapper.Map<ContactRes>(entity);
}
public ContactRes Update(int contactId, ContactReqEdit dto)
{
var entity = FindContactIfExists(contactId, true);
_mapper.Map(dto, entity);
_repositoryManager.Save();
return _mapper.Map<ContactRes>(entity);
}
Delete Contact
The Delete method does two things.
- Delete Contact and the related tables
- Delete the profile picture from Cloudinary
We are just calling ContactRepository.Delete() method. It will delete the Contact entity and all its related data from child tables.
Lets have a look at the database diagram first. The Contact has zero to many relationship with 6 other tables. When we create a new Contact, we just add new row in Contact table, we don’t save anything in related tables. We have other 6 repositories for creating phone, email etc.
But when we delete a Contact and call ContactRepository.Delete() method, it will automatically delete the data from its child tables. Well, this is the behavior that we want. If a Contact has 2 phone numbers, an email address and a website, we just show these data in the Delete page and ask user for confirmation. We won’t stop user and ask him to first delete all his phone numbers one by one, all his addresses and his emails etc. and then delete. No, this is not suitable in this case.
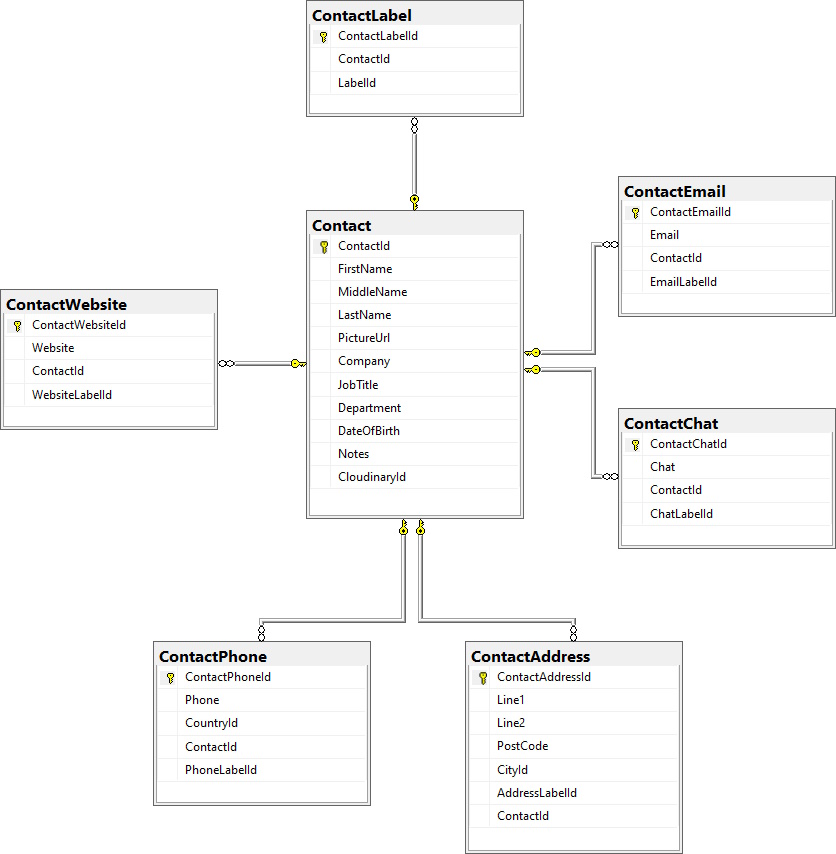
When we created the related tables Contactlabel, ContactPhone, ContactEmail etc. we added non null ContactId as foreign key. Due to this, the Entity Framework adds cascade delete behavior, so that when we delete Contact, it will also delete all its child records.
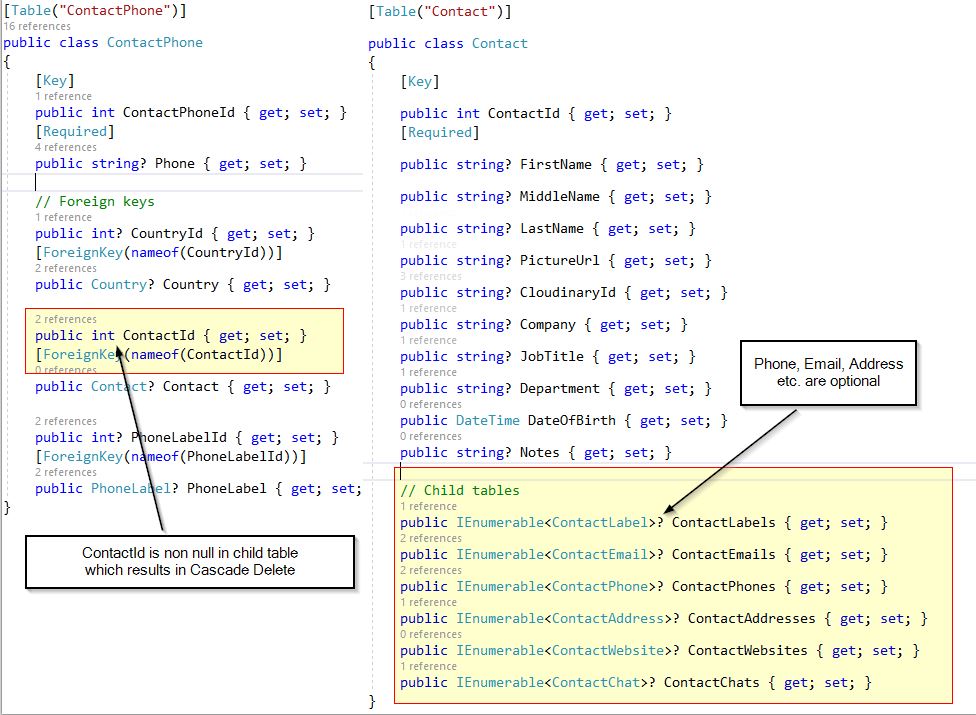
When we look at the code below, there is one Delete method call, it deletes child records automatically. No need to call Delete method 6 times on its child tables.
public void Delete(int contactId)
{
var entity = FindContactIfExists(contactId, true);
_repositoryManager.ContactRepository.Delete(entity);
_cloudinaryService.DeleteImage(entity.CloudinaryId);
_repositoryManager.Save();
}
Remember that when we were deleting City, we added a validation to count addresses, in which that city id is used. And we threw exception if a CityId existed in some address. If we don’t throw exception in this validation, deleting a City would also delete all the addresses, which would result in unwanted data loss. In that case, we don’t want cascade delete and are performing validation before delete. But in Contact, we want to do cascade delete.
Search and Get Contact
Nothing special in search and get service methods. The service methods just call the repository methods. The Search contact method query was complex, as it had where conditions in all the related tables, directly related and 2-4 distant related as well e.g. Contact.ContactAddress.Any(x => x.City.State.Country.Name.Contains(searchText)). This was handled in the Repository class, because it is related to the database, SQL, LINQ. This makes our service methods simple.
private Contact FindContactIfExists(int contactId, bool trackChanges)
{
var entity = _repositoryManager.ContactRepository.FindByCondition(
x => x.ContactId == contactId, trackChanges)
.FirstOrDefault();
if (entity == null) { throw new Exception("No contact found with id " + contactId); }
return entity;
}
public ContactRes Get(int contactId)
{
var entity = FindContactIfExists(contactId, false);
return _mapper.Map<ContactRes>(entity);
}
public ApiOkPagedResponse<IEnumerable<ContactRes>, MetaData> Search(ContactReqSearch dto)
{
var pagedEntities = _repositoryManager.ContactRepository.
Search(dto, false);
var dtos = _mapper.Map<IEnumerable<ContactRes>>(pagedEntities);
return new ApiOkPagedResponse<IEnumerable<ContactRes>, MetaData>(dtos,
pagedEntities.MetaData);
}