This is the 10th article in the ASP.NET with Entity Framework beginner series. In previous articles we covered a lot of basic and necessary things that should be part of any web API project. We did not cover exception handling so far. In this article we will talk about how to configure exception handling in ASP.NET web API.
If we throw exceptions, ASP.NET adds extra information like error in line number, inner exception and other details. It converts the Exception object to Json using default implementation and we get a lot of information in the http response body.
We can handle exceptions using built in ASP.NET middleware and customize the error message. In our app, we just want to send the error message that we used in Exception constructor e.g. throw new Exception(“No person found with id ” + personId). It can be done using extension methods like we did for configuring CORS, repositories etc.
Open Extensions\ServiceExtensions.cs file and add a new method as follows.
public static void ConfigureExceptionHandler(this IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseExceptionHandler(c => c.Run(async context =>
{
var exception = context.Features
.Get<IExceptionHandlerPathFeature>()
.Error;
var response = new { error = exception.Message };
await context.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(response);
}));
}
In this extension method, we used this IApplicationBuilder instead of IServiceCollection, because the exception middleware is configured at app level.
In the response, we only get exception.Message, the exact string that we use while throwing exception. In the end, we set this message as response.
To register this exception middleware extension method, open Program.cs file. Call this method just before app.Run in the last.
app.ConfigureExceptionHandler();
app.Run();
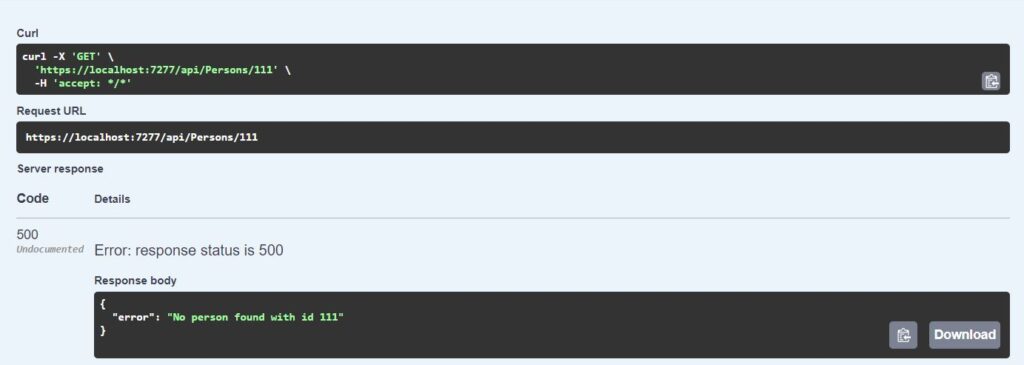
Now run the project and open the Swagger default UI. Try the Get person API with an invalid id, you will now get the exact error message.