This is the 6th article in the React client beginner series, in which we call web API using Axios. In previous article, we created Person List page, which fetched all records from the web API and displayed all records in Table component. In this article you will learn how to use Formik to input data for create and edit Person.
DTOs for Create and Edit Person
For reference open the ASP.NET web Api project. Open Dtos\Person.cs file. We created PersonReqEdit dto class. This Dto is used for both create and edit person.
In React side we will also create these Dto classes, so that we can send data to our Api. In React project, open src\Dtos\Person.ts file. Add the following class in it.
export class PersonReqEdit {
firstName?: string;
lastName?: string;
phoneNumber?: string;
gender?: string;
}
Axios API for Create and Edit Person
After creating Dtos, we need to define create and edit methods in person Service helper class. Person Service helper class uses Axios for http requests. And our React pages will use the service helper classes. React components should not know about Axios. React components should only know about the Service Helper classes like PersonApi.
Open src\api\personApi.js and add the create method as follows.
create: async function (person) {
const response = await api.request({
url: `/persons`,
method: "POST",
data: person,
})
return response.data
},
The create function takes person as parameter and pass it to the web API in POST request.
update function is similar to the create function. It has one extra parameter for the personId, the id of person whom we want to update. Second parameter is Person data in PersonReqEdit Dto. Both are sent to the web API using PUT http request. Add the update method in src\api\PersonApi.js as follows.
update: async function (personId, person) {
await api.request({
url: `/persons/` + personId,
method: "PUT",
data: person,
})
},
We will also need get method, which takes personId as parameter and returns a single PersonRes dto. This method is required to populate the Edit form with existing data. The code snippet for the get method is given below.
get: async function (personId) {
if (!personId) return {};
const response = await api.request({
url: `/persons/` + personId,
method: "GET",
})
return response.data
},
Edit Person component
Now that we have created Dtos and service helper methods for create and update, we will create the UI for editing the person. Add a new file PersonEdit.tsx in src\persons. Type rafce and insert the template code.
Create and Edit UI are same, so we will use the same component PersonEdit.tsx for both creating and editing the Person. The Url will determine whether we are creating a new person or editing an existing one.
- http://localhost:3000/persons/edit – Create a new person
- http://localhost:3000/persons/edit/1 – Edit an existing person whose personId is 1
urlParams to get personId
React has useParams hook to get the url parameters. We will use it to get the personId from the Url. Update the PersonEdit.tsx as follows.
const PersonEdit = () => {
const params = useParams();
const personId = params.personId;
const updateText = personId ? "Update Person" : "Add Person";
console.log("person id: " + personId)
console.log(updateText)
return (
<>PersonEdit</>
);
}
export default PersonEdit
In url http://localhost:3000/persons/edit/1, the personId is 1. How do React knows that 1 is the personId?
The answer is in the Routing that we define in App.tsx. Previously we set the routes for / and /persons url. Open App.tsx again to add url routes for edit person.
<BrowserRouter>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Layout />}>
<Route index element={<Home />} />
{/* Persons */}
<Route path="persons">
<Route index element={<Persons />} />
<Route path="edit" element={<PersonEdit />} />
<Route path="edit/:personId" element={<PersonEdit />} />
</Route>
</Route>
</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>
/ is the main Route. persons is a child of /. persons has children of its own, edit and edit/:personId. In React :personId in route is a variable, that can have any text value. This value of this variable can be accessed from the urlParams hook. Save all files and run the app using npm start, if not already running. Click on Persons menu on top. Open browser Console window. Click on Add Person button, it will open http://localhost:3000/persons/edit. Console should show the following output.
person id: undefined
Add Person
Go back to the Person list and now edit a person by clicking on Edit link of any record. The console windows should now show the following output
person id: 1
Update Person
How do we decide if we are creating or editing?
The variable personId, that we get from urlParams, will decide. If personId is undefined, we are creating new person. If personId has some value, then we are editing existing person.
Load existing person if exists
In create mode, we will display an empty form to the user. In update mode, we will fill the form with data of the existing person. When personId has some value, we will call our web API to get single user. The best way to call API on page load in React is to do it in useEffect hook. Open PersonEdit.tsx and add the following code, after the person state variable.
useEffect(() => {
loadPerson();
}, [personId]);
const loadPerson = () => {
if (personId) {
PersonApi.get(personId).then(res => {
setPerson(res);
console.log(res);
})
}
}
Note the [personId] in the useEffect. It means whenever personId values changes, useEffect hook will be executed.
If we just use empty braces like [], then the useEffect hook will be executed only once on page load.
In loadPerson function, we are calling the API helper method to get a single person. Run the program with different urls like
- http://localhost:3000/persons/edit/1
- http://localhost:3000/persons/edit/111
- http://localhost:3000/persons/edit/1987 etc.
If the personId is valid, we will get person response from the API. If the personId is not found, the web API will return error message. The code will work fine, the form will be empty if we pass an invalid Id. We will handle errors later, for now we will continue with create and edit form.
Form validation schema with Yup
We will use two npm packages in this page.
- Formik for creating form
- Yup for form validation
Lets start with data validation with the Yup package first. Open PersonEdit.tsx and add a new Yup object as follows.
// Formik validation schema
const validationSchema = Yup.object({
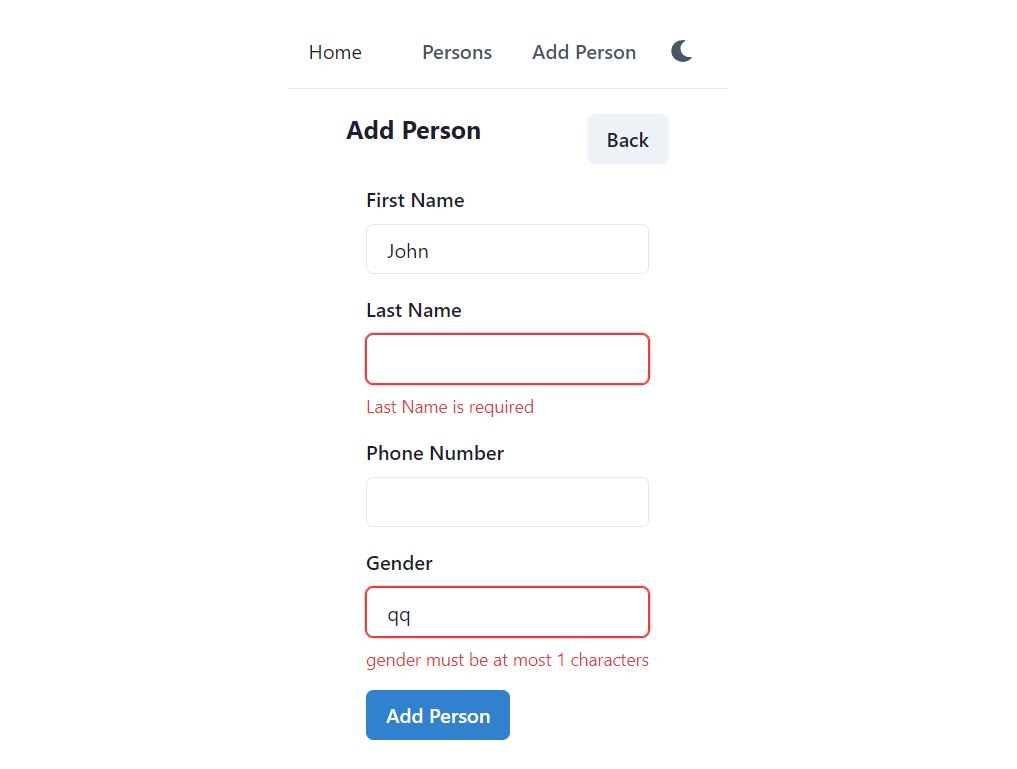
firstName: Yup.string().required("First Name is required").max(100),
lastName: Yup.string().required("Last Name is required").max(100),
phoneNumber: Yup.string().max(20),
gender: Yup.string().max(1),
});
This Yup schema is same as our PersonReqEdit dto, which is same as the PersonReqEdit dto in the web API.
In ASP.NET web API, we added built-in validation attributes directly in the Dto like [Required] and [MaxLength]. In React, there is no built-in validation or robust Form component. So we use Yup for validation and Formik for building Form.
Why use Validation in React?
The web API has data validation at Service and Entity (database) level. We can surely send invalid data to the API, the API will throw error. But it will take a server round trip from client to the API for sending data, then receiving error messages. If we perform data validation in React, it will be very fast.
When using client side library like React, Next, Angular etc. which use single page application, they do not reload the whole page when URL changes. They only render what is updated. They only fetch contents from the server or API when absolutely needed. We add client side validation to compliment this behavior, we perform simple validation like required, max length etc. on client side.
Submit Form to the web API
We have not created the form yet. First we declared the Form validation schema with Yup. Lets handle the submit part first as well. The form submission and validation are independent of Form building/loading.
Add submitForm method in PersonEdit.tsx as follows
const submitForm = (values: PersonReqEdit) => {
// console.log(values);
if (personId) {
updatePerson(values);
} else {
createPerson(values);
}
};
const updatePerson = (values: PersonReqEdit) => {
PersonApi.update(personId, values).then(res => {
navigate("/persons")
});
};
const createPerson = (values: PersonReqEdit) => {
PersonApi.create(values).then(res => {
navigate("persons")
});
}
Our form will call submitForm method and pass Person Edit Dto as parameter. We will create form soon. submitForm decides whether we want to create a person or update a person, based on personId. It uses a simple condition to call createPerson or updatePerson.
createPerson just takes Dto and sends POST request to the web API. While updatePerson takes personId and Dto, and sends PUT request to the web API. The http requests are handled in the API helper, so our Edit page is simple.
Edit Page layout – Display page heading and form
So far, we handled url parameters to set personId, loaded person from API if Id is valid, called submitForm for creating/updating the person. All these are operations, without any UI. Lets build the Form UI now.
To build the form UI, lets start with defining the page layout as follows.
return (
<Box width={"100%"} p={4}>
<Stack spacing={4} as={Container} maxW={"3xl"}>
{displayHeading()}
{showUpdateForm()}
</Stack>
</Box>
);
The layout is similar to the List all Persons page. Heading on top and then Form. Add displayHeading method as follows.
const displayHeading = () => (
<Flex>
<Box>
<Heading fontSize={"xl"}>{updateText}</Heading>
</Box>
<Spacer />
<Box>
<Link
ml={2}
as={RouteLink}
to={"/persons"}
>
<Button colorScheme={"gray"}>Back</Button>
</Link>
</Box>
</Flex>
);
It uses the combination of Box and Flex layout. Heading is at left, Link is aligned right. The left over space is consumed by the Spacer.
Create Form with Formik
We have used four properties in the Formik component.
- initialValues – set to the person state variable of type PersonRes. It will be set if personId has value. Formik will initialize the form fields with this object.
- onSubmit – we get the form input data in object, which we pass it to submitForm, we already created this method.
- validationSchema – we already have created Yup object and added validations in it
- enableReinitialize – we set it to true, this is useful if we change person state variable. The form will update its fields automatically based on the values of person state variable
The code snippet is given below.
const showUpdateForm = () => (
<Box p={0}>
<Formik
initialValues={person}
onSubmit={(values) => {
submitForm(values);
}}
validationSchema={validationSchema}
enableReinitialize={true}
>
{({ handleSubmit, errors, touched, setFieldValue }) => (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
</form>
)}
</Formik>
</Box>
);
We have initialize Formik component and also declared the form above. The form takes some props like touched, errors etc. We will see these in action soon. Lets add form body now and define the fields. Below code snippet contains the firstName field.
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<Stack spacing={4} as={Container} maxW={"3xl"}>
<FormControl isInvalid={!!errors.firstName && touched.firstName}>
<FormLabel htmlFor="firstName">First Name</FormLabel>
<Field as={Input} id="firstName" name="firstName" type="text" />
<FormErrorMessage>{errors.firstName}</FormErrorMessage>
</FormControl>
</Stack>
</form>
We use Chakra UI’s FormControl component to render the form field. Formik can integrate well with Chakra UI. The FormControl has isInvalid property to render validation error. We set the isInvalid property to true based on errors.firstName. If firstName has validation error, FormControl will mark it as invalid.
Inside FormControl there are 3 child components
- FormLabel – It is Chakra UI component, it sets the label, which is text
- Field – It is Formik component, rendered as Chakra UI’s Input component. It binds to person state variable, which we used as Formik’s initialValues
- FormErrorMessage – displays validation error messages using Yup’s validator
We define all fields in this way. We used simple text properties in this basic example, so all fields will be defined in the same way as firstName.
You can find the complete code for PersonEdit.tsx at https://github.com/saqibrazzaq/efcorebeginner/blob/main/Person/react-client/src/persons/PersonEdit.tsx.
The code for Edit Person component is complete now. Lets summarize the workflows for create and edit modes.
Create new Person workflow
- Open Url without personId in params e.g. http://localhost:3000/persons/edit
- personId is undefined
- person state variable will also be initialize with all empty strings
- Formik will initialize with empty person
- User enters data in fields
- Validation is done, error messages will be displayed if any
- User presses submit button, Formik will pass form values to submitForm method
- personId is undefined, so create person web API will be called
Edit an existing Person workflow
- Open Url with personId in params e.g. http://localhost:3000/persons/edit/1
- person state variable initialized with all empty strings
- personId set to 1
- useEffect hook will call get person web API
- if get person API returns error, person state variable will keep in empty state
- if get person API returns a valid result, person state variable will set to Person Response Dto
- Formik will initialize the form fields with person data
- User enters data in the fields
- Validation is done
- user presses submit button, Formik will pass updated values to the submitForm method
- personId is 1, so update person web API will be called
This way with very few changes, we have implemented both Create and Update person in the same React component. In most cases, Create and Update will use the same page, as they both are similar operations. UI is also same, so we do not need to create separate page for Edit.
If in any scenario, the Edit operation is different than the Create, then it is suitable to create separate UI components for Create and Update.
Run the web API and React client app using npm start. Try creating new person and update them, it should work with all validations.
In the next article, we will create the delete page.